Description
Nebulizers are medical devices used to deliver aerosolized medication directly to the lungs. They are commonly prescribed for respiratory conditions such as asthma, COPD, bronchitis, and cystic fibrosis. The nebulizer turns liquid medication into a mist, making it easier for the lungs to absorb.
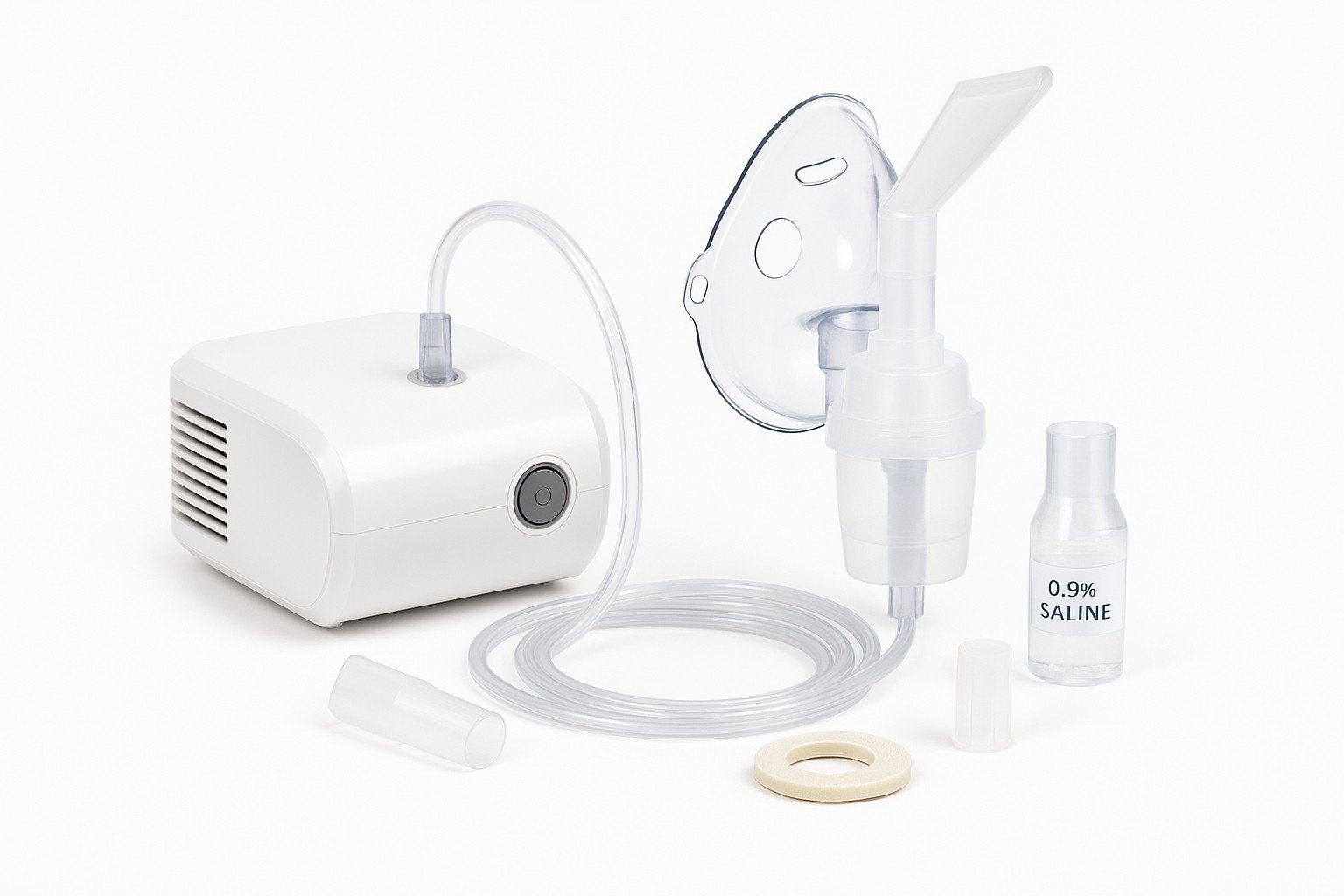
Key Components of Nebulizer Equipment
1. Nebulizer Machine (Compressor)
-
Powers the nebulizer by using compressed air to generate mist.
-
Types of compressors:
-
Jet Nebulizers – Use compressed air; effective but typically louder.
-
Ultrasonic Nebulizers – Use sound waves; quieter and faster.
-
Mesh Nebulizers – Use a vibrating membrane; quiet, portable, and efficient.
-
2. Nebulizer Cup (Medication Cup)
-
Holds the liquid medication.
-
Connects to the tubing and mouthpiece or mask for aerosolization.
3. Mouthpiece or Mask
-
Mouthpiece – Best for adults or older children who can inhale deeply.
-
Face Mask – Suitable for children or those unable to use a mouthpiece; covers nose and mouth.
4. Tubing
-
Connects the compressor to the medication cup.
-
Carries compressed air needed to create the mist.
5. Filters
-
Found in the nebulizer machine.
-
Must be replaced regularly to maintain performance and prevent contamination.
Nebulizer Supplies
1. Medication for Nebulizers
-
Bronchodilators (e.g., Albuterol) – Open airways during asthma attacks or COPD flares.
-
Corticosteroids (e.g., Budesonide) – Reduce airway inflammation.
-
Saline Solution – Loosens mucus and hydrates airways.
2. Saline Solution
-
Often used alone or with medications.
-
Helps hydrate the airway and enhance medication delivery.
3. Cleaning Solutions and Kits
-
Nebulizer Cleaning Solutions – Special disinfectants for daily or weekly cleaning.
-
Cleaning Brushes – Help reach and clean small parts inside the cup and tubing.
4. Replacement Parts
-
Medication Cups and Tubing – Replace every 2–3 months.
-
Masks and Mouthpieces – Replace every 3–6 months depending on use.
-
Filters – Replace based on manufacturer’s instructions (typically every 1–3 months).
5. Humidifiers or Oxygen Accessories
-
Patients with chronic lung diseases may use nebulizers with:
-
Oxygen concentrators
-
Humidifiers to prevent airway dryness
-
6. Travel Bags
-
Provide organized, portable storage for nebulizers and accessories.
-
Ideal for on-the-go treatments or travel use.
Cleaning and Maintenance
-
After Each Use:
-
Wash the cup, mask, or mouthpiece with warm soapy water.
-
Rinse thoroughly and air-dry.
-
-
Weekly Disinfection:
-
Use a vinegar-water solution (1:3) or manufacturer-recommended cleaner.
-
Soak for 20 minutes, rinse well, and let air dry.
-
-
Regular Replacement:
-
Replace disposable parts to prevent bacterial buildup and ensure effective treatment.
-
-
Changing Filters:
-
Check and replace filters as needed to maintain optimal air quality and performance.
-
Choosing the Right Nebulizer
-
Portability:
-
Handheld and battery-operated nebulizers are ideal for travel or frequent use.
-
-
Noise Level:
-
Mesh and ultrasonic nebulizers are quieter than traditional jet models.
-
-
Treatment Time:
-
Mesh and ultrasonic options usually deliver medications more quickly.
-
-
Ease of Use:
-
Select models that are easy to assemble, clean, and operate, especially for children or elderly users.
-
When to Use a Nebulizer
Nebulizers are recommended for individuals who:
-
Have difficulty using inhalers
-
Require frequent or long-term respiratory therapy
-
Are managing:
-
Asthma attacks
-
COPD exacerbations
-
Bronchitis or respiratory infections
-
Cystic fibrosis
-
Chronic lung conditions
-





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.